Carotid Ultrasound - Nagender Reddy, MD, FACC
Item Number: 541
Time Left: CLOSED
Value: $456
Online Close: May 15, 2009 11:00 PM EDT
Bid History: 0 bids
Description
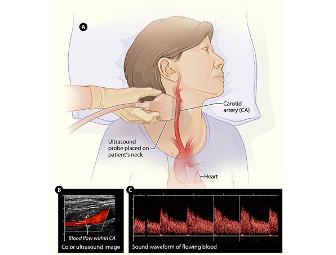
The carotid ultrasound is most frequently performed to detect narrowing, or stenosis, of the carotid artery, a condition that substantially increases the risk of stroke.
The major goal of carotid ultrasound is to screen patients for blockage or narrowing of their carotid arteries, which if present may increase their risk of having a stroke. Once the diagnosis is made a comprehensive treatment may be initiated.
It may also be performed if a patient has high blood pressure or a carotid bruit (pronounced brU-E)—an abnormal sound in the neck that is heard with the stethoscope. Other risk factors calling for a carotid ultrasound are:
- advanced age
- diabetes
- elevated blood cholesterol
- a family history of stroke or heart disease
A carotid ultrasound is also performed to:
- locate a hematoma, a collection of clotted blood that may slow and eventually stop blood flow.
- detect dissection of the carotid artery, a split between layers of the artery wall that may lead to obstruction of blood flow or a weakening of the wall of the artery.
- check the state of the carotid artery after surgery to restore normal blood flow.
- verify the position of a metal stent placed to maintain carotid blood flow.
Doppler ultrasound images can help the physician to see and evaluate:
- blockages to blood flow (such as clots)
- narrowing of vessels (which may be caused by plaque)
- tumors and congenital malformation
Special Instructions
Expiration 5/15/10
Please make appointment with Barbara Brown, Manager mailto:www.bbmma@hotmail.com
316 SE 12th Street, Bld. #100
Ocala, Florida 334471
Phone 352-401-9888